Toggle Navigation
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a process transforming a piece of material into a specified shape by following coded programmed instructions and without a manual operator directly controlling the machining operation.CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing technology that automatically removes material from raw stock based on a set of computer-generated instructions. This technology automates precision cutting, drilling, milling, and turning processes, offering a high level of accuracy and consistency in manufacturing parts.
Here are key aspects of CNC machining:
How It Works:
CNC machines interpret design files (usually CAD models) and execute a series of automated instructions to produce parts with exact dimensions. This removes the need for manual control.
Common CNC Processes:
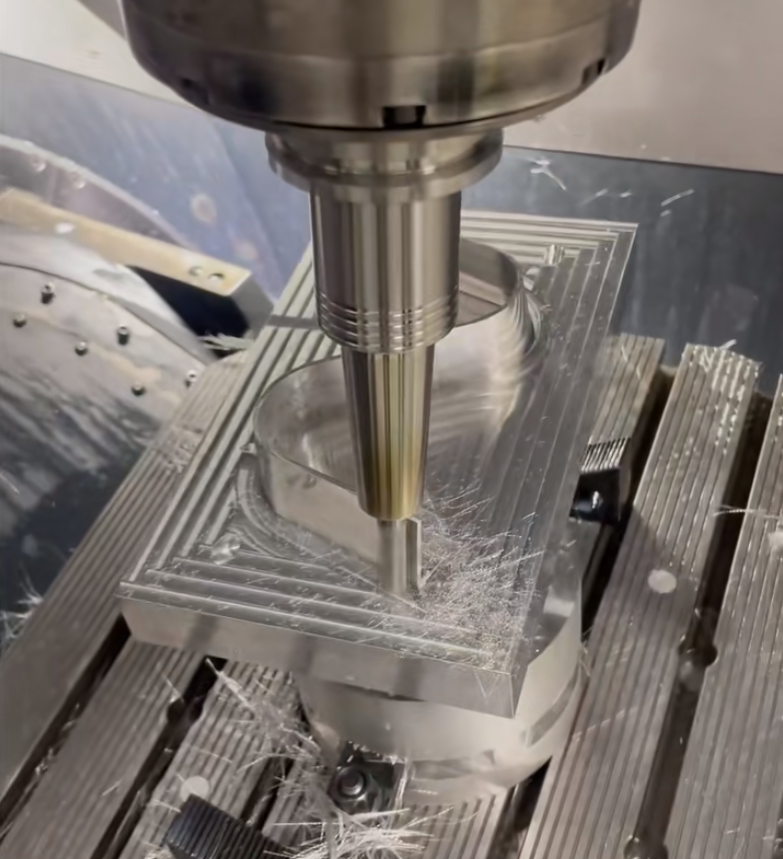
Milling: Rotating cutting tools are used to remove material from the workpiece.
Turning: The workpiece is rotated while a cutting tool shapes it, often for cylindrical objects.
Drilling: Precise holes are drilled into the material.
Grinding: This involves smoothening and finishing surfaces with an abrasive wheel.
3. The advantages of cnc machining
High Precision and Accuracy: CNC machines operate with extreme precision, often achieving tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm. This makes them ideal for producing complex components that require intricate detailing.
Repeatability: Once a CNC program is created, the same product can be replicated consistently with no variations, ensuring high quality across production runs.
Increased Efficiency: CNC machines can operate continuously and are typically faster than manual processes. They can also perform multiple operations in a single setup, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Complex Designs: CNC machining can handle complex geometries and shapes that would be difficult or impossible with manual methods. This makes it especially useful in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
Material Versatility: CNC machines can work with a wide variety of materials, including metals (like aluminum, steel, brass and titanium), plastics, etc.
Flexibility in Prototyping and Production: CNC machining can easily transition from prototype to production, providing flexibility for both one-off custom jobs and mass production.
4. Applications:
Aerospace and Automotive: For creating engine parts, custom tools, and components.
Medical: Producing precision medical devices and instruments.
Electronics: Manufacturing parts for devices and enclosures.
CNC machining is a core part of manufacturing for many industries and aligns well with Accuteck’s custom hardware and machining capabilities.