Toggle Navigation
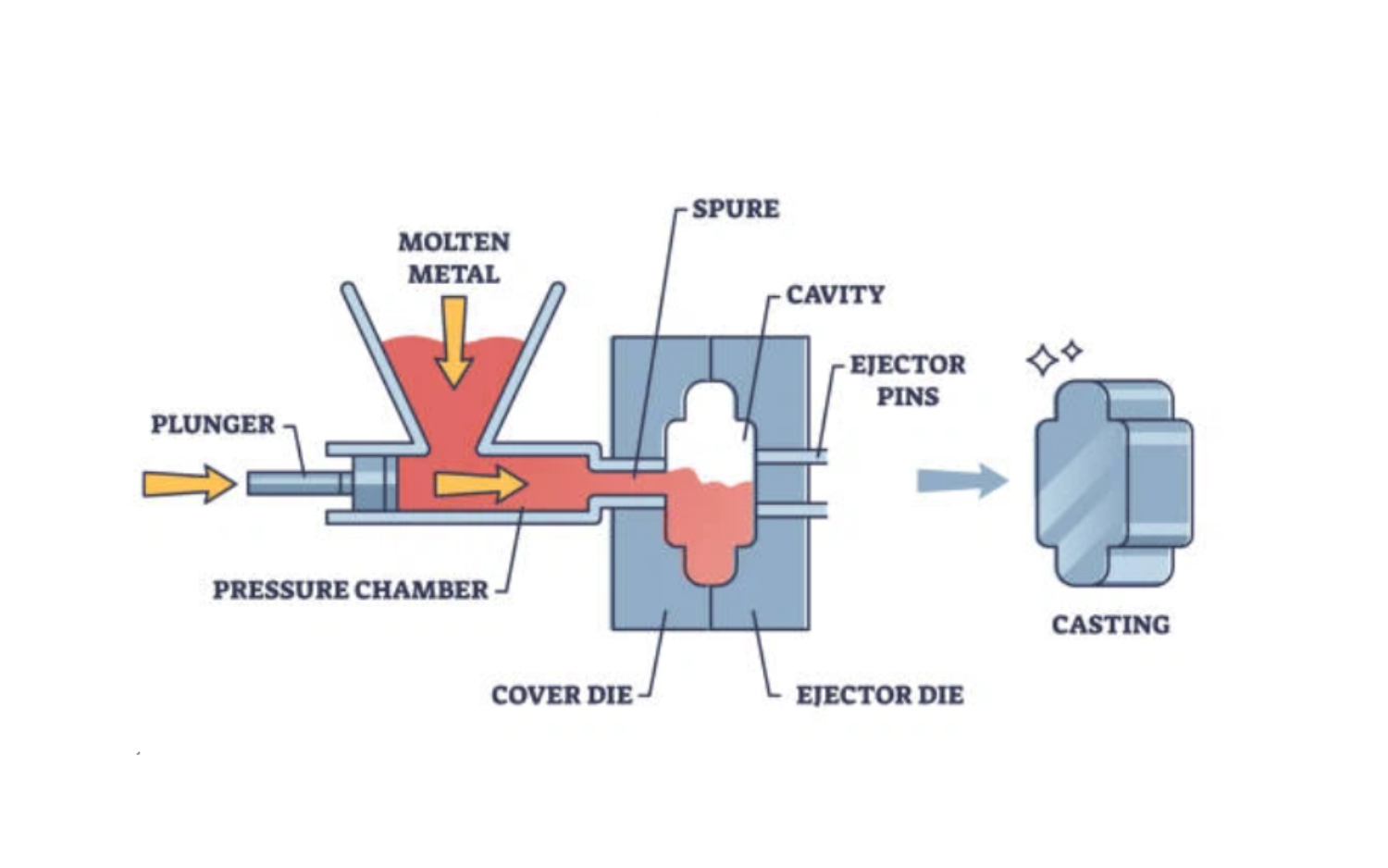
Die casting is a manufacturing process in which molten metal is forced into a mold cavity under high pressure.
The molds, also known as dies, are typically made from steel and can producecomplex, high-precision metal parts at a fast rate.
This process is widely used for making parts from metals such as aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys.
The casting process implements a steel mold often capable of producing tens of thousands of castings in rapid succession.
The die must be made in at least two sections to permit removal of castings.
The casting cycle begins with the two die halves are clamped tightly together by the die casting press.
Molten aluminum is injected into the die cavity where it solidifies quickly.
These sections are mounted securely in a machine and are arranged so that one is stationary while the other is moveable.
The die halves are drawn apart and the casting is ejected.
Die casting dies can be simple or complex,having moveable slides, cores, or other sections depending on the complexity of the casting.
Most machines use mechanisms actuated by hydraulic cylinders to achieve locking. Others usedirect acting hydraulic pressure.
Die casting machines, large or small, vary fundamentally only in the method used to inject molten metal into the die.
Molten Metal Injection: Metal such as aluminum, zinc is melted and injected into a mold cavity at high pressure.
Cooling and Solidification: The molten metal quickly cools and solidifies within the mold, taking the shape of the die cavity.
Ejection: Once solidified, the mold is opened, and the part is ejected from the die.
Casting equipment and molds are expensive, so the die casting process is generally only used to mass-produce large quantities of products.
Manufacturing die-cast parts is relatively easy, generally requiring only four major steps, with a low incremental cost per unit.
Die casting is particularly suitable for manufacturing large quantities of small and medium-sized castings,
making it the most widely used of various casting processes.
Advantages of die casting include:
High precision and accuracy: It enables the creation of parts with tight tolerances and smooth finishes.
Complex shapes: It can produce intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through other manufacturing methods.
High production rate: Suitable for mass production as the molds can be reused many times.
Good mechanical properties: The parts made through die casting are strong, durable, and resistant to wear.
Compared to plastic injection molding, die casting uses metal instead of plastic, resulting in stronger, more durable parts.
Unlike sand casting, die casting is more precise and offers a better surface finish, though it is more suitable for high-volume production due to higher tooling costs.
Die casting is ideal for industries needing high-precision, strong, and lightweight metal parts. It is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, construction and consumer goods.